芯片验证基础
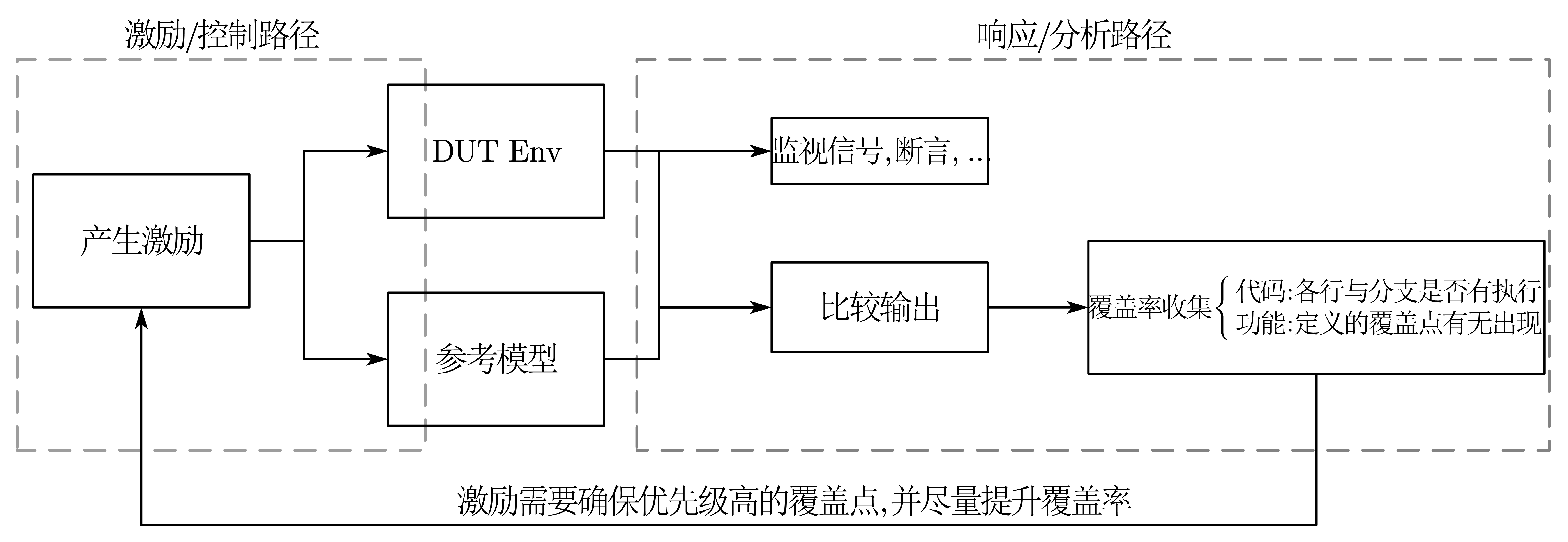
验证框架 以FIFO为例
先用picker工具将Verilog转化为对应语言的dut(这里是Python). --rw 1写入波形文件, -c开启覆盖率:
picker export FIFO.v --sname FIFO -w FIFO.fst --lang python --sim verilator --rw 1 -c
pytest运行python写的测试:
python -m pytest . -sv --toffee-report
如果用--toffee-report选项, 每次运行会在reports/生成覆盖率报告与波形文件
testcase and fixture
用pytest运行装饰符所标志的testcase, fifo_env为环境, fifo_agent是对接口的包装, 直接异步调用fifo_agent的驱动方法
@toffee_test.testcase
async def test_with_ref(fifo_env: FIFOEnv):
await fifo_env.fifo_agent.exec_reset()
await fifo_env.fifo_agent.exec_write(random.randint(0, 2**32 - 1))
await fifo_env.fifo_agent.exec_read()
对于testcase出现的fifo_env, 会调用同名的fixture方法来创建: 实例化dut, 绑定bundle到dut的管脚与内部信号, 并将bundle传入FIFOEnv, 接上参考模型RefModel(), 添加定义好的功能覆盖组
@toffee_test.fixture
async def fifo_env(toffee_request: toffee_test.ToffeeRequest):
# create dut
this_dut = toffee_request.create_dut(DUTSyncFIFO, "clk")
toffee.start_clock(this_dut)
# create and bind bundles
writeBundle = WriteBundle().bind(this_dut)
readBundle = ReadBundle().bind(this_dut)
# bind internal signals
InternalBundle.counter = this_dut.GetInternalSignal('SyncFIFO_top.SyncFIFO.counter')
internalBundle = InternalBundle()
internalBundle.bind(this_dut)
# create env and attach reference model
fifo_env = FIFOEnv(readBundle, writeBundle, internalBundle)
fifo_env.attach(RefModel())
# add coverage groups
toffee_request.add_cov_groups([
get_cover_group_basic_operations(fifo_env.fifo_agent),
get_cover_group_fifo_state(fifo_env.fifo_agent),
get_cover_group_pointer_compare(fifo_env.fifo_agent)
])
yield fifo_env
驱动 监测与对照 (参考模型使用函数调用模式)
FIFOAgent定义了用装饰符@driver_method()标志的驱动方法, 通过env.agent.bundle来为dut提供激励.
@driver_method()
async def exec_write(self, data):
self.write.enqueue(data)
self.read.re.value = 0
print(f"[dut] append {data:x}")
await self.monitor_step()
装饰符@monitor_method()标志了监测方法, 一个周期中, 监测方法先于驱动方法执行
@monitor_method()
async def monitor_output(self):
output = {
'data': self.read.data.value,
'empty': self.read.empty.value,
'full': self.write.full.value
}
return output
对每个驱动方法, 参考模型都有对应的驱动钩子函数, 有相同的格式(参数与返回值). 如果函数有返回值, 每次执行时都会对比驱动方法与钩子函数的返回值是否相同. 驱动钩子函数默认在驱动方法之前执行. 对监测方法, 其对应的监测钩子函数会将监测方法的返回值作为额外的参数.
@driver_hook("fifo_agent.exec_write")
def push(self, data_i):
# if (we_i & !full_o) write
if not self.is_full():
self.queue.append(data_i)
print(f"[ref] append {data_i:x}")
@monitor_hook("fifo_agent.monitor_output")
def monitor_output(self, output):
print(f"\033[1;32;40m [dut] 0x{output['data']:016x}\t[ref] 0x{self.dataout:016x}\033[0m")
功能覆盖点定义与覆盖率收集
行覆盖率的收集是picker自带的功能, 使用picker生成dut时添加-c选项. 使用verilator_coverage处理.dat文件生成.info文件, 再用lcov的genhtml命令生成html报告. 如果使用toffee, 运行测试时添加--toffee-report选项即可.
功能覆盖率的统计需要使用toffee.funcov中的类来自定义CovGroup->CovPoint->CovBin, toffee_test.reporter.set_func_coverage的函数来添加agent的CovGroup. 这里要区分功能覆盖率模型与参考模型, 前者观察dut的行为从而记录覆盖情况, 后者对照标准输出与dut输出判断是否正确 -> 验证的完备性与正确性是分开的.
收集功能覆盖率通常涉及以下核心元素:
- 覆盖组(CovGroup): 一个逻辑容器, 用于组织一组相关的覆盖项, 对应验证计划中的一个高层功能点(例如,“FIFO 基本读写操作”)或一个接口
- 覆盖点(CovPoint): 用于监视设计的某个特定行为、变量值或一组变量值的组合(例如,“FIFO 计数器的值” “写操作时的状态”)
- 覆盖区间/仓(CovBin): 覆盖点对应信号的具体数值、数值范围、状态转换或条件
例如, Basic operations覆盖组包含了Write operation, Read operation, No operation 3个覆盖点, 观察读写事务; 分别对应write_occurs, read_occurs, no_operation 3个覆盖仓, 通过观察dut的信号来判断是否发生读写事务.
def get_cover_group_basic_operations(agent: FIFOAgent) -> CovGroup:
group = CovGroup("Basic operations")
group.add_watch_point(agent.write, {"write_occurs": check_write_operation}, name="Write operation")
group.add_watch_point(agent.read, {"read_occurs": check_read_operation}, name="Read operation")
group.add_watch_point(agent, {"no_operation": check_none_operation}, name="No operation")
return group